Module 2
Integrating Academic and Career Development
Short description
The module reviles the impact of the work integrated learning and the role of the career counselor in bridging the gap between STEM skills sought after by employers and those supplied by academic institutions.
Although many of in-demand STEM skills can be acquired through self-study, higher education is still considered prestigious by society and preferred by many employers.
A quality workforce, is a product of university-business collaboration!
Here are the main reasons why to develop and upgrade your understanding and knowledge on the field:
- The Integrating Academic and Career Development enhances the employability by providing students hands-on experience and opportunities for becoming valuable industry insights and building professional networks.
- The Integrating Academic and Career Development promotes partnerships with business, industry and government, which improves the economic growth of the country (Matoti, Junqueira and Odora 2011).
- The Integrating Academic and Career Development enhances the university's reputation and enables Academica to share their research with the business.
- The Integrating Academic and Career Development give students a greater sense of purpose and motivation, making their education more meaningful and attractive.
The module suggests also some strategies for career counsellors on how to support the university-industry cooperation and ensure 21st century skills development in students.
Bridging the Gap Between Academic Knowledge and Real-World Skills
To learn driving from books without practice is not possible. However, education and knowledge on the rules of the road, safe driving behaviour standards, providing first aid or basic car service skills are essential to take the driving licence and get on the road. To become a master chef just by reading recipes is also unlikely and even less likely to get hired at a reputable restaurant. Theory and practice go hand in hand!

Today, employers, educational institutions, and governments are facing the challenge to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge gained in academic settings and the practical skillsets demanded by the digital STEM labour market. Despite the growing interest of young people for career in the field of information technology, for example, and the worldwide rise of STEM graduates, 77% of the EU companies report difficulties in finding workers with the necessary skills (https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/europe-fit-digital-age/european-year-skills-2023_en) The first step to close this gap is to identify what specific skills do STEM employers look for.
Identifying Skill Gaps
Jobs positions posted in one major Bulgarian online job search platform and in the EURopean Employment Services (EURES) portal have been analysed to identify specific skills increasingly sought after by digital STEM employers. 10 vacancies for each STEM disciplines were studied and the most frequently required digital skills are listed below as in high demand. The results have shown that specialists with the following technical skills are widely sought across the SCIENCE sector:
- Programming in Python
- Performing data analysis by the use of MATLAB, Python, Visual 3D/Inspect 3D
- Comfortable using of a variety of digital platforms such as Office 365, Toddle and Classter
In the TECHNOLOGY sector sought after are technical skills like:
- Use of simulation software
- Use of well-established software development tools for documentation
- Product design tools
Employers offering jobs for ENGINEERS are looking for workforce with the following skills:
- Programming in C, SQL, Python
- Use of simulation software
- Project management tools
According the posted vacancies found by the keyword Mathematics, most in demand are skills like:
- Programming in Python, Java or C++
- Image processing algorithms
- Big Data
Soft skills sought-after by digital STEM employers include:
- Organization/ Time management
- Communication
- Teamwork
Summarized, the scanning of the job listings has shown that strong skills in coding languages, use of data analysis tools and simulation software, are in high demand by digital STEM employers. According many online published surveys, the three most sought-after programming languages in Europe to diverse industry needs are Python, C++ and JavaScript. Regarding the big data analytics tools, proficiency in SAS, Python or Tableau is crucial for jobs seekers in the STEM sector. It is foreseen that the EU simulation software market will grow at a CAGR of 13.50% during 2024-2032. That means, the labour market will need even more professionals in Autodesk, Ansys and MATLAB.
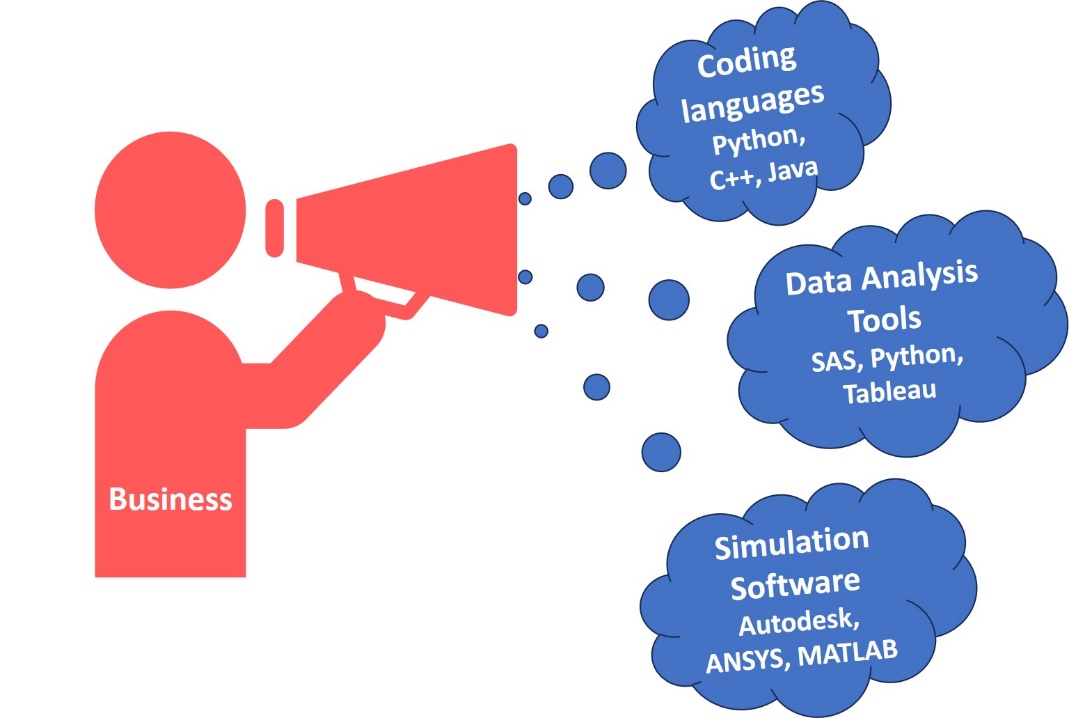
The online tool Skills-OVATE (Skills Online Vacancy Analysis Tool for Europe, https://www.onetonline.org/find/stem?t=0), developed by the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP), offers detailed information on the skills and job roles most sought after by employers across 32 European countries. The data are collected from thousands of sources, including private job portals, public employment service portals, recruitment agencies, online newspapers and corporate websites and updated four times per year. Based on the provided by Skills-OVATE information, bellow are presented in demand technological skills for occupations required education in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines. In the brackets are given the so-called HOT Technologies or the technologies most frequently included across all employer job postings.
- Analytical or scientific software (Ansys Fluent; CERN Physics Analysis Workstation PAW; COMSOL Multiphysics; The MathWorks MATLAB; Wolfram Research Mathematica)
- Development environment software (C; Eclipse IDE; Microsoft Azure software; Microsoft Visual Studio)
- Graphics or photo imaging software (Adobe Photoshop; GNU Image Manipulation Program GIMP; Ploticus)
- Object or component-oriented development software (C++; Oracle Java; Perl; Python)
- Presentation software (Microsoft Power Point)
- Computer aided design CAD software (Autodesk AutoCAD; CD-adapco STAR-CAD; Dassault Systemes CATIA; PTC Creo Parametric)
- Accounting software (Deltek Costpoint; Fund accounting software; Hyperion Enterprise)
- Electronic mail software
- Document management software
- Medical software
- Geographic information system (ESRI ArcGIS software; Geographic information system GIS software)
- Enterprise resource planning ERP software system
- Desktop communications software (Eko)
It is seen, that the labour market in the STEM sector needs advanced digital skills, i.e. skills in designing, developing, managing and deploying technologies such as high-performance computing, artificial intelligence and cybersecurity.
Exercise: Choose a specific digital STEM field. Research at least 3 online job postings for entry-level positions in this field. Point out at least 5 essential technical skills and 3 soft skills frequently mentioned in job descriptions. Enrich your own knowledge on the selected as in-demand by employers advanced digital skills to better analyze individual's skill sets and experience related to them and evaluate students’ potential for career development in professional areas, in which the identified skills are required.
The second step to bridge the gap between academic knowledge and real-world skills, requires reforms in the education and training systems addressed by The European Commission through the Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027). One of the most important strategies to increase the academic education quality and efficiency is to integrate physical engagement into the learning process. Hands-on learning allows students to gain practical experience and develop labour market relevant skills.

Source : https://pixabay.com/photos/hand-palm-skin-fingers-dirty-3588162/
Exercise: Read the Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027), https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A52020DC0624, and familiar yourself with the initiatives and investments undertaken by the EU in digital skills development and further gender gap decrease in the technology and entrepreneurial sector. Learn more about the EU Commissions pilot project Digital Opportunity Traineeships that aims at giving higher education students and recent graduates the opportunity to gain hands-on professional experience in digital fields demanded by the labour market. What is the European Digital Education Hub? Which key activities provides the Hub to facilitate the collaboration across education and training sectors.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a process of learning through direct experience and reflection. Hands-on learning opportunities in STEM disciplines include internships, research projects, laboratory experiments, field studies, and competitions. These activities allow learners to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations.
The approach of experimental learning is distinct from rote or didactic learning, where learners play a passive role, and emphasizes the importance of reflection and personal involvement in the learning process.
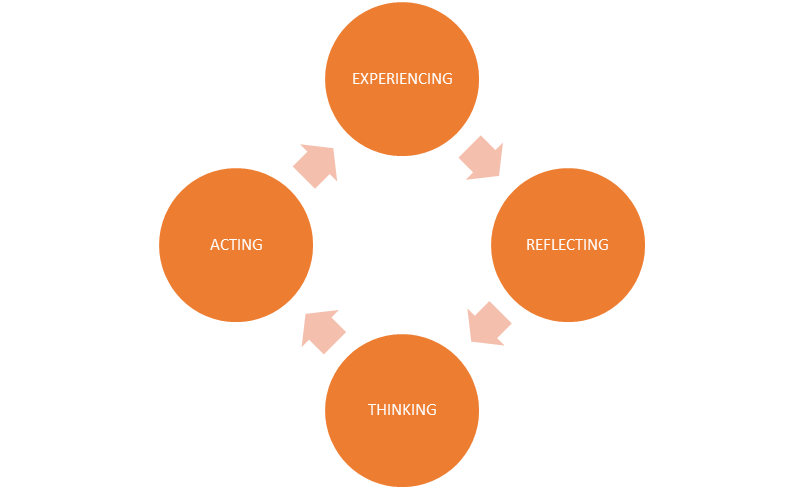
The experiential learning cycle is a natural and organic process that people engage in life situations without realizing they are learning. This cycle is composed of two pairs of opposite modes: Experiencing and Thinking, and Reflecting and Acting. People tend to have preferences for how they use this cycle, focusing on certain modes more than others. However, when individuals deliberately engage with all four modes, deep learning occurs.
The Four Modes of the Experiential Learning Cycle are:
1. Experiencing: Directly engaging with life situations and experiences.
2. Thinking: Reflecting on the experiences and analysing the information.
3. Reflecting: Processing the information and identifying key takeaways.
4. Acting: Applying the knowledge and skills gained from the experience.
To achieve deep learning, it is essential to deliberately engage with all four modes of the experiential learning cycle. This approach allows individuals to fully process and apply what they have learned, leading to more effective learning outcomes.
Experiential learning offers numerous benefits for learners:
1. Improved Communication and Collaboration: Collaborative experiential activities enhance communication skills, teamwork, and the ability to work effectively with others.
2. Personalized Learning: Experiential learning allows students to interact with information in a way that is meaningful to them, making learning more personal and engaging.
3. Creativity and Problem-Solving: Hands-on activities encourage students to think creatively and develop problem-solving skills by seeking their own unique solutions.
4. Reflection and Analysis: Reflective observation is an integral part of experiential learning, enabling students to analyze their actions, outcomes, and how they differ from others.
5. Mistakes as Learning Opportunities: Experiential learning involves trial and error, helping students learn from their mistakes and develop resilience.
6. Accelerated Learning: Hands-on activities require practice, problem-solving, and decision-making, leading to accelerated learning and improved retention.
7. Guided Discovery: Experiential learning helps students discover their passions and aptitudes, guiding them toward future career paths.
8. Preparation for Adult Life: Experiential learning activities, such as team projects, prepare students for adult life by teaching them to work effectively, lead, and adapt to changing circumstances.
9. Increased Self-Esteem and Empowerment: Experiential learning enhances students' self-esteem and sense of self-efficacy, leading to increased motivation and engagement in learning.
10. Improved Academic Outcomes: Research shows that experiential learning leads to better retention, higher test scores, and a deeper understanding of subject matter beyond mere facts and figures.
11. Enhanced Prosocial Behaviours: Experiential learning increases students' likelihood to engage in prosocial behaviours and decreases their likelihood to engage in at-risk behaviours.
While the integration of the experiential learning as a mandatory teaching method in the school and higher education depends on national governments, what can students themselves do to gain practical experience and apply what they have learned in real-world situations?
There are numerous programmes providing students with opportunities to attend on research projects, short internships, STEM competitions or to conduct volunteer work. Below are listed some of them as well as online portals offering hands-on learning opportunities focused on the development of in-demand digital skills.

- ErasmusIntern.org is part of an Erasmus Student Network (ESN) project. It provides an integrated market place that aims at bringing together internship providers and students seeking an internship opportunity abroad. Under https://erasmusintern.org/traineeships?page=1 STEM students can search for a remote or in person internship based on their field of study, degree, language skills, program duration and commitment.
- AIESEC is a global platform for young people offering them internships, volunteering opportunities, and more. AIESEC is a worldwide student-run organization that generates over 6,000 paid internships each year in nearly 90 countries.
- DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service) provides summer internship program for undergraduate students in the fields of biology, chemistry, physics, earth sciences and engineering. The program DAAD RISE (Research Internships in Science & Engineering) offers opportunities for undergraduate students to work with research groups at universities and top research institutions across Germany for a period of 2 to 3 months during the summer. Graduating seniors and graduate students are eligible for RISE Professional. DAAD provides also a lot of scholarships for student to participate or develop their own research project getting guidance from established scientists.
- EU-LISA Security Unit Internship - the European Union Agency for the Operational Management of Large-Scale IT Systems in the Area of Freedom, Security and Justice offers six-month paid experience at EU-LISA in Tallinn, Estonia for recent university graduates who are at the beginning of their professional career in the area of computer and information sciences, mathematics and related.
- ESA Student Internships - the European Space Agency offers each year student traineeships from 3 to 6 months to students in their final or second-to-last year of a Master's degree in technical and non-technical domains.
- IAESTE Internships - the International Association for the Exchange of Students for Technical Experience offers internships with duration 8 and 52 weeks for young people around the world to gain experience and increase chances for employment in the area of computer and information sciences, chemistry, material science, and chemical engineering, mechanical and civil engineering, geology, architecture, mathematics and statistics, physics, business, management, and marketing.
- NATO Internship Programme offers internships with duration six months in the Allied Air Command (AIRCOM) located in Ramstein, Germany for students completed at least two years of their Bachelor's or Master's Degree, or recent graduates (degree obtained within the last 18 months) of Computer Science, Engineering or a related field.
- RWTH Aachen UROP International provides undergraduate students with opportunities to conduct research programs at RWTH Aachen University for around two months over the summer. The majority of the projects are in the fields of science and engineering, as mathematics, architecture, and the social sciences.
- WiRe - Women in Research is a fellowship programme for international female postdoctoral researchers at the University of Münster in Germany with duration 4-8 months, which offers fellows access to all communication channels, networks and research infrastructure of the university, so that they can perform their research idea, boost their research communication skills and share experience.
- EU TalentOn - is a new event that challenges young talented researchers to find solutions to help solve the most pressing global issues. The four-day event brings together early career researchers and features an extensive programme, co-created with academia, innovators and industry. Winners receive sponsored prizes from the EU, industry and mentors.
- Maximo Nivel, International Volunteer HQ (IVHQ), GoEco, Projects Abroad are some examples of travel organizations offering internships or volunteer work in the STEM sector.
Beside the lack of practical experience, what also leads to insufficient work force with competencies relevant to the labour market needs, is that in-demand specific skills are not necessarily taught by educational institutes. In today's world, continuous updating of curricula or upskilling teachers’ knowledge is costly and largely ineffective (Rathelot and van Rens, 2017) as the digital landscape changes rapidly.
The incorporation of real industrial projects into the educational environment, is an effectively strategy to bridge the gap between academic knowledge and business needs driven by the digital transformation. In the next section are presented some successful examples of universities-companies cooperations that have provided/provide graduates with more relevant knowledge and skills by giving them opportunities for hands-on or lifelong learning.
Integrating Industry Projects
DEMOLA PLATFORM (Finland) is an excellent example of university–business collaboration model for R&D and product development. The project was financed through the City of Tampere Business Development Programme (2006-2011) ‘Creative Tampere’ and won in 2010 the AER Innovation Award. Through him students from the three regional universities were engaged in solving challenges sourced from the business. The cooperation between the higher education institutions and the companies were organized in the following way:
- Students were assigned a real-life problem from the project partners, under which several organizations from the public sector, small, medium-sized and large-scale international enterprises (for example, the global semiconductor chip maker, Intel).
- The student team(s) started working on the problem.
- If the provided by the students’ results have satisfied the company, it either has licensed shared right or purchased all rights for itself.
The key results of Demola highlight the engagement of over 500 students in developing product and service concepts as more than 10% of them were headhunted. 96% of the completed projects were licensed, new jobs have been created and new companies have been established. Within the project, in excess of €500,000 has been awarded to students.
Currently, there are eight Demola centres in six countries.
Fishing for Experience is a practical programme offered by the Hamburg University of Technology (TUHH), Germany, that brings together students, graduates and alumni with attractive companies in the Hamburg metropolitan region. In small international and interdisciplinary teams, the students work, 5 – 6 months parallel to their studies, on entrepreneurial issues. An example of a project offered through the program over the summer semester 2024 is briefly described below.
The HAMBURG WASSER Group supplies Hamburg and some surrounding communities with drinking water and treats the wastewater in the region. Together with company employees, students will work on the creation of switch-on procedure to restart the Hamburg wastewater treatment plant after a blackout. The task includes obtaining, processing and analysing of data, standardisation of wastewater values, determination of the process-engineering boundary conditions for the commissioning of the individual process stages.
Acua Limited (UK) is a pioneering university Employer Engagement Project, established in 2008 with the financial support of The Higher Education Funding Council for England. Later, it grew into a limited company, trading subsidiary of the Coventry University, focused on the delivery of higher education meeting the needs of its corporate clients. The required by the business specific knowledge and skills were embedded into current or planned programmes at the Coventry University, certificated or developed into new academic majors. In 2015 Acua Limited was dissolved. For the time of its business activity, more than 100 blue chip companies across a wide range of public and private sectors used her services to develop together a talent pool of nearly 10,000 employees. In 2012 Acua Limited won the British Chambers of Commerce Award.
WIGRATEC is a cooperation between small and medium-sized companies located in Germany and Niederland, the University of Magdeburg and the Anhalt University, funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. The collaboration provides students from the both universities chance to work on the development of new technologies and equipment for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries as a part of their bachelor/master thesis.

Source: https://pixabay.com/photos/handshake-hand-give-business-man-2056023/
Strategies to equip students with the needed skills for STEM careers
Career counsellors can support the development of in-demand digital skills by STEM students, by encouraging them to self-taught education and extracurricular STEM activities. Alongside their academic coursework, students can get equipped with the needed for STEM careers digital skills by taking part in online courses, workshops, clubs, camps, mentorship programs, virtual labs and discussion groups.

Source: Adapted from https://pixabay.com/photos/adult-education-a-book-books-2706977/
Online courses, training programs or other activities, relevant to the mentioned above in-demand skills in coding languages, use of data analysis tools and simulation software, can be found on the following web platforms:
- Codecademy, https://www.codecademy.com/, offers free coding classes in 12 different programming languages, including Python, Java, Go, JavaScript, Ruby, SQL, C++, C# or Swift.
- Python.org, https://devguide.python.org/: This is the official website for Python, and it provides a comprehensive tutorial for learning Python, along with detailed documentation on the Python language.
- Udemy,https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=programing: Udemy is an online learning platform offering a wide range of Python courses for beginners and advanced learners.
- Code.org, https://code.org/students, offers app, game, and web labs for students to learn coding and STEM-related fields.
- Coursera Inc., https://www.coursera.org/, is an American global massive open online course provider. Phyton For Everybody, Introduction to Programming with Python and Java, Python 3 Programming, Data Science: Foundations Using R, are some of the courses offered by Coursera Plus. Many of the them are free, but for official certification users have to paid.
- FutureLearn, https://www.futurelearn.com/, offers a wide variety of paid and free online courses, as for example in Phyton, Java, Tableau and many others.
- edX, https://www.edx.org/learn/simulation, offers a range of simulation courses that provide hands-on, virtual experiences to equip students with practical skills through interactive learning scenarios. These courses cover topics such as crafting virtual realities, enhancing decision-making, and navigating ethical dimensions. Students can choose from introductory to advanced levels and even participate in simulation projects.
- Ansys Innovation Courses, https://courses.ansys.com/: Ansys offers comprehensive skill-building courses that provide just-in-time and on-demand learning. These courses include video lectures, practical exercises, and quizzes to help students develop skills in simulation software.
- Computer Vision Tutorial, PylmageSearch, https://pyimagesearch.com/, and OpenCV Tutorial, https://opencv.org/university/courses/, offer online courses and tutorials in image processing and computer vision in Python for beginners and experienced professionals covering.
There are also several online courses for developing of in-demand by STEM employers’ soft skills as for example FutureLearn, Clss Central, edX, Coursera, etc. Students should be encouraged to participate in debates, oral presentations or to engage in public speaking to enhance their verbal and written communication skills. Teamwork and time management, as another increasingly soft after by STEM employers’ skills, can be improved by participation in group projects and activities that require collaboration, use of time-management tools, familiarization with techniques like Pomodoro, Eat That Frog, Getting Things Done (GTD) or The 80/20 Rule that have been proven to help people manage their time more effectively.
According to Harvard Business Review, women only apply to positions that they are 100% qualified for, whereas men will apply if they are only 60% qualified. This confidence gap is even more prevalent in the tech world.
So, mapping a well-rounded education pathway to STEM careers is another core element in the process of overcoming the shortage of labour force with advanced digital skills.
Mapping academic pathways to digital STEM careers
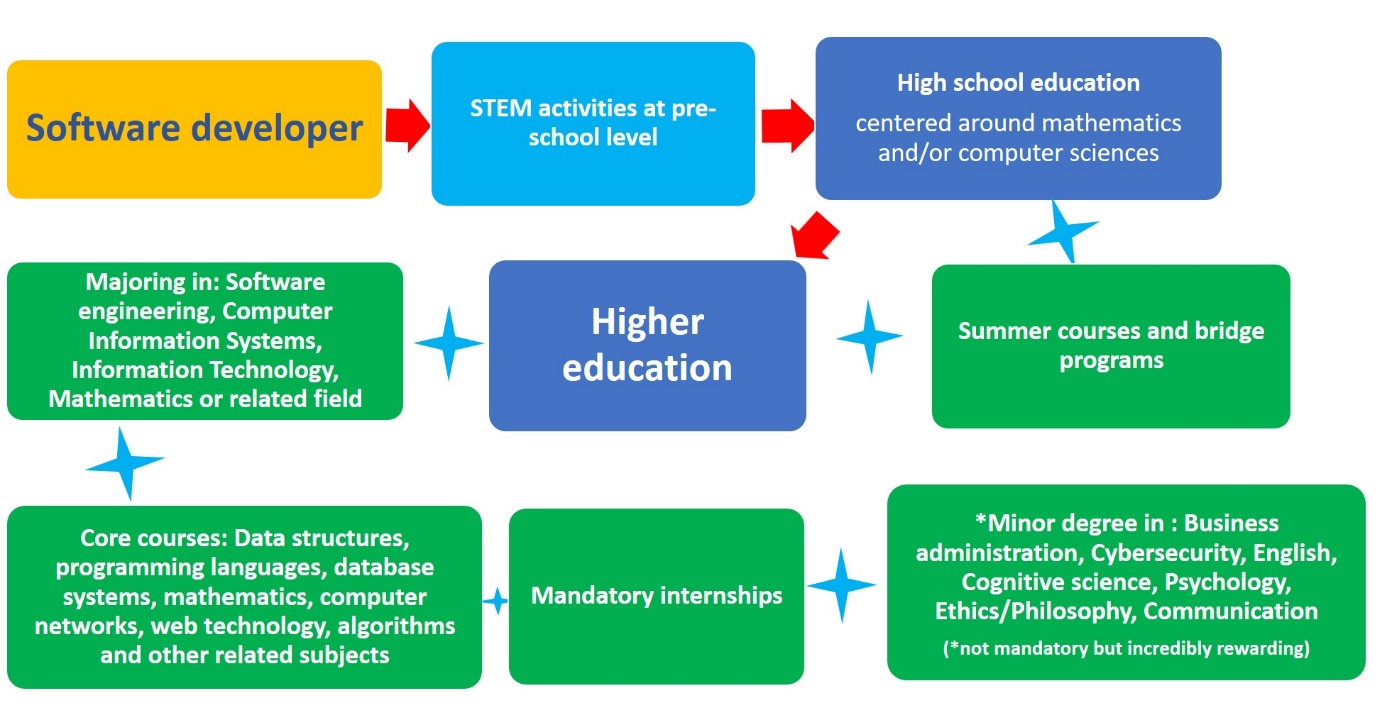
The software developer has been identified by the Future women project as one of the most trending and most wanted professions in Europe in the field of the digital economy and STEM. How to become a software developer can involve many different routes - from self-taught developer to graduate degree-holder. Since most companies and more specialised roles require bachelor degree as a minimum qualification, below is presented the academic pathway to become a Software developer.
Getting a job as a software developer typically starts with earning a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field. STEM activities at pre-school level or high education centred at mathematics and/or computer since might be advantageous during the study or when applying for a job. Furthermore, a study provided by the United Kingdom (ASPIRES, 2013) has found that students who do not express STEM-related aspirations at age 10 are unlikely to develop STEM aspirations as they get older.

Source : https://pixabay.com/photos/chemistry-baby-experiment-science-5632650/
The core classes at the university include data structures, programming languages, database systems, mathematics, computer networks, web technology, algorithms and other related subjects. The obtaining of a minor degree is not mandatory but provides a comprehensive, well-rounded education. The choice of the minor subject depends on individual career goals and interests. For example, if the student plans to menage or run a startup, a second education in the field of finance/accounting and or marketing/sales is recommended.
Exercise (individual or group exercise) – Choose one of the following professions - business intelligence analyst, digital marketing manager, IT security specialist or data analyst and create such academic pathway map. Expand it to a master’s degree. What does it take students to succeed this academic pathway? What aptitudes, skills, personal characteristics, or interests do students in this program tend to have?
As mentioned, there is no “right way” to become a software developer. But what can be down to encourage more young women to choose the academic over the self-taught route for their career development? One answer to this question lies in the modernization of the education system. According a Google study, emerging trends that educators must closely monitor in the future are presented in the next section.
The Future of Learning – trends, mix, etc.
The rapidly changing digital landscape demands that academic organizations adapt their learning and development strategies to stay competitive and prepare students with skills adequate to the labour market needs. Trends that promise to make education more accessible, attractive, effective and relevant to the demands of the 21st century include:
- Remote, online, hybrid and lifelong learning
- Bite-sized Learning (Microlearning)
- Exam management with education technology
- Personalized learning
- Project-based oriented education
- Creation of AI-powered learning environments
- Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) into the learning process
- Gamification
- Social-emotional Learning

In conclusion
In the context of development practical skillsets in student demanded by the digital STEM labour market and fostering STEM graduate employability, the role of the career counsellor consists in:
- Identifying current and future labour market needs. Analysis of skills supply, demand and mismatch. Interpretation of the data for various customer needs.
- Providing labour market information to families, high school students undergraduates, education institutions and companies.
- Promoting good practices based on university - business relationships.
- Being informed about new policy initiatives and programs supporting universities-industry cooperation and transmitting them to stakeholders.
- Advertising the fact that individuals making higher-education choices today have higher potential for career growth and success in supervisory roles.
- Engendering educational aspirations in STEM disciplines.
- Encouraging students to extracurricular STEM activities.
- Fostering intrinsic motivation in STEM students to lifelong learning.
- Suggesting well-defined educational roadmaps.
- Supporting student access to more challenging STEM education.
The career chancellors’ services are an important source of collaborative expertise for integration of Career Development Learning into curriculum!
Quizzes
External resources
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/eu-simulation-software-market-21755 - Europe Simulation Software Market Overview Source
https://experientiallearninginstitute.org/what-is-experiential-learning/ - What is experimental learning?
https://www.xaa.edu.sg/blog/students/experiential-learning-benefits/ -- Benefits of the hands-on learning
file:///C:/Users/Professional/Downloads/Case_Study.pdf - Demola: Open innovation platform, case study
file:///C:/Users/Professional/Downloads/final_report2017.pdf, THE state of university-business cooperation in Europe, final report
file:///C:/Users/Professional/Downloads/casestudyreport.pdf - 30 good practice case studies in university-business cooperation
https://joint-research-centre.ec.europa.eu/index_en?prefLang=bg - On the Futures of
Technology in Education: Emerging Trends and Policy Implications, a JRC Science for policy report
file:///C:/Users/Professional/Downloads/wcms_534314.pdf - Guide to anticipating and matching skills and jobs
file:///C:/Users/Professional/Downloads/EDU-WKP(2020)17.en.pdf - The role of labour market information in guiding educational and occupational choices
file:///C:/Users/Professional/Downloads/EJ1235633.pdf - Integrating career development learning into the curriculum: Collaboration with the careers service for employability, a research article by Ruth Bridgstock, Michelle Grant-Iramu and Alan McAlpine