Module 4
Digital economy and STEM entrepreneurship
Short description
The objective of this module is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the digital economy and STEM entrepreneurship, presenting the knowledge, skills, and mindset needed to succeed in the evolving landscape of technology-driven innovation and business. It aims to illuminate the transformative impact of technology on economies, industries, and entrepreneurial opportunities.
This module will explore the complex relationship between STEM disciplines and entrepreneurship, reinforcing learning through practical applications. Through the process of envisioning, designing, and developing a viable business model in STEM domains, the module aims to enhance entrepreneurial skills and understanding of digital economy opportunities.
Learning outcomes of the module:
- In terms of knowledge:
- You will understand the core concepts and components of the digital economy.
- You understand the impact of digitalization on various sectors, and economies.
- You will understand the STEM fields with entrepreneurial ventures, recognizing opportunities for innovation and business creation within STEM disciplines.
- In terms of skills:
- You will apply critical thinking, analytical skills, and creative problem-solving methodologies within STEM entrepreneurship contexts.
- You will demonstrate effective communication and presentation abilities to articulate and pitch STEM startup ideas coherently and persuasively.
- You will acquire skills to develop and evaluate comprehensive business models tailored for STEM ventures, assessing feasibility and scalability.
- In terms of Responsibility:
- You will develop a sense of responsibility for your own environment by actively seeking out new business ideas.
- You will develop a sense of responsibility for further development in the digital economy and your own business ideas.
- In terms of Attitudes:
- You will gain an entrepreneurial mindset emphasizing adaptability, resilience, creativity, and a willingness to take calculated risks in problem-solving.
- You will cultivate an orientation towards innovation, encouraging you to take a proactive approach to problem-solving and the pursuit of novel solutions
Digitalization and Digital Transformation and Its Effects
Digitalization and Digital Transformation are two interconnected concepts reshaping modern businesses and industries. Digitalization refers to the adoption and integration of digital technologies into various aspects of an organization's operations, processes, and products/services, enabling them to become more efficient, agile, and data-driven. On the other hand, Digital Transformation is a broader strategic initiative that encompasses not only the adoption of digital technologies but also a fundamental change in business models, organizational culture, and customer experiences to adapt and thrive in the digital age. According to a study by Deloitte on digital transformation, successful organizations leverage digitalization as a stepping stone towards broader transformational goals, focusing on innovation, customer-centricity, and operational excellence. Another report by IDC emphasizes the importance of digital transformation strategies in driving growth, competitiveness, and resilience in today's dynamic business environment. Overall, digitalization lays the foundation, while digital transformation drives holistic organizational change towards digital maturity and sustainable success.

Digitization and digitalization have significantly grown, especially with the rise of new organizations and the booming startup age. The impact of digital technology on business processes has transformed various industries and the entire consumer market.
Some countries like India boasts a high level of digital awareness with a strong presence of coders and top organizations, it still has a way to go to achieve full digitization.
Key aspects of how digitization impacts businesses
Increased Efficiency: Digital tools and automation have streamlined business processes, allowing organizations to achieve higher efficiency levels and allocate resources to more impactful tasks.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Digital platforms enable real-time collaboration and information sharing, improving teamwork, transparency, and productivity.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Digitization generates vast amounts of data that can be analyzed for valuable insights, enabling informed decision-making and optimized operations.
Improved Customer Experience: Digital channels provide personalized and seamless customer experiences, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty, albeit with higher customer expectations.
Agility and Adaptability: Digital processes empower businesses to be agile and responsive to market changes, crucial in today's fast-paced environment.
Innovation and Disruption: Digital technologies foster innovation and disruptive business models, allowing startups and small businesses to compete with established players.
Cybersecurity Challenges: Increased digital reliance necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to protect data, systems, and customer information from cyber threats.
What is Digital Economy
The term "digital economy" refers to the economic activities that result from connecting persons, businesses, devices, data, and operations using digital technology. It refers to the online interactions and transactions that occur across various sectors and technologies, including the internet, mobile technology, big data, and information and communications technology.
All successful, adaptive organizations in the twenty-first century are typically powered by digital technology. Simply put, digital transformation is enabling businesses to use the latest technology to help them achieve their goals, but faster, more efficiently, and more profitably.
A digital economy is built on digital platforms that facilitate business processes and enable better economic value. Hyperconnectivity is the backbone of digital business, expanding the connections between people, organizations, and machinery through the internet, mobile technology and IoT.
“Uber, the world’s largest taxi company, owns no vehicles. Facebook, the world’s most popular media owner, creates no content. Alibaba, the most valuable retailer, has no inventory. And Airbnb, the world’s largest accommodation provider, owns no real estate… Something interesting is happening.”
Source: TechCrunch
Hyperconnectivity, defined as online links between people, businesses, devices, and data, drives the digital economy. It challenges conventional business structures and connections. Companies such as Uber, Facebook, Alibaba, and Airbnb demonstrate creative models that challenge industry boundaries and value propositions. They prioritize data utilization, innovative services, and cultural shifts in management. These companies have taught us how to use data for transformation, focus on service innovation, and adapt to fluid roles in an ever-changing digital context. Adopting digital transformation pillars such as data use, service innovation, and job flexibility is critical to success in the digital economy.
The image below shows in which sectors digital jobs can be actively pursued.
Source: The World Economic Forum
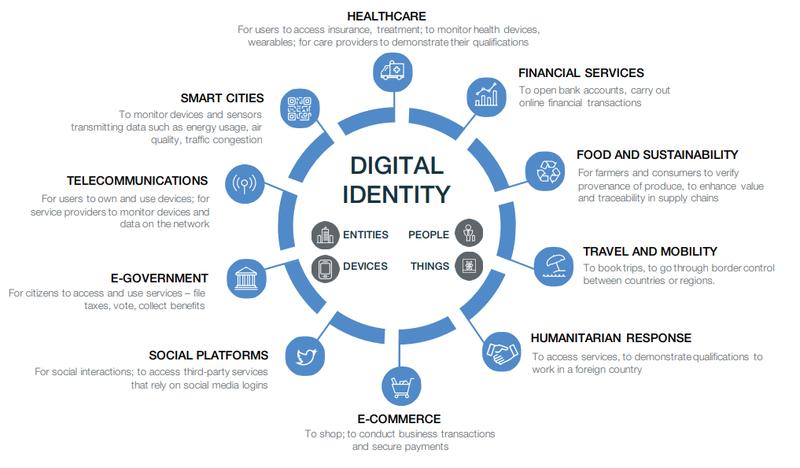
Key elements of a digital economy
A digital economy encompasses a range of elements that collectively shape and define its landscape. Here are some key elements of a digital economy:
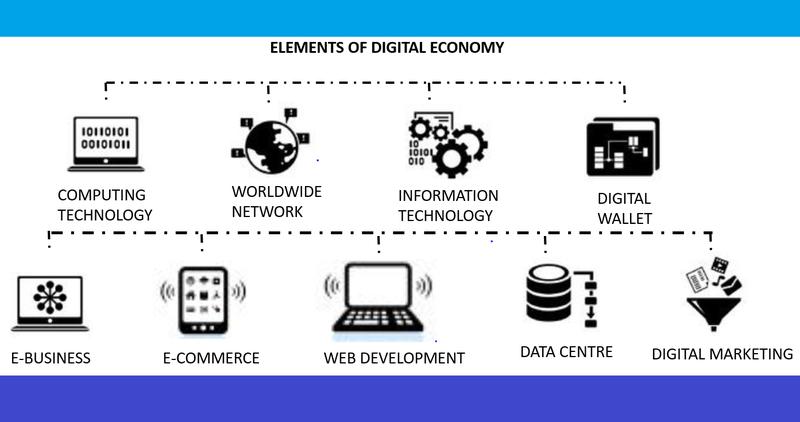
Source: Medium, https://www.ir.com/guides/the-importance-of-the-digital-economy
These elements interact and evolve dynamically, shaping the opportunities, challenges, and transformations within the digital economy across industries, societies, and global markets.
The main enablers of the digital economy
The digital economy is crucial in creating global marketplaces and driving innovation across industries in today's interconnected and fast expanding world. The digital economy is fundamentally dependent on various factors that enable firms, consumers, and governments to utilize digital technologies for economic development and societal progress. These facilitators include a wide array of technology infrastructure, expertise, rules, and innovative ecosystems that together constitute the foundation of digital transformation. Comprehending and utilizing these factors are crucial for companies and economies to flourish in the digital era, where connectivity, data-driven insights, and agile decision-making are of utmost importance. Examining the main factors that facilitate the digital economy provides insight into the fundamental components that propel digital innovation, competitiveness, and sustainable development in the 21st century.
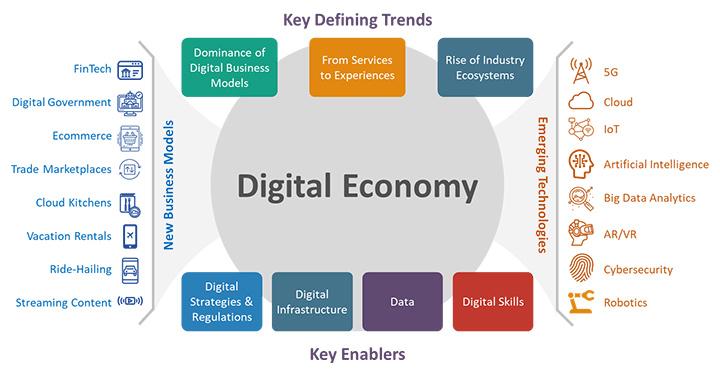
Source: www.canva.com
The main enablers of the digital economy encompass a range of factors that drive growth, innovation, and connectivity in digital ecosystems. These enablers include:
Digital Infrastructure:
| Data Analytics and AI:
|
E-commerce and Digital Payments:
| Mobile Technologies:
|
IoT (Internet of Things):
| Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT):
|
Digital Skills and Talent:
| Regulatory Environment:
|
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
| Digital Marketing and Customer Engagement:
|
Which technologies are accelerating the digital economy?
There are many technologies are playing key roles in accelerating the digital economy by driving innovation, efficiency, and new business models. Some of the primary technologies include:
Cloud Computing: Enables businesses to access and use computing resources (like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics) over the internet. Cloud computing promotes scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and global accessibility for digital services and solutions.
Internet of Things (IoT): Connects everyday devices (such as sensors, wearables, appliances, vehicles, industrial equipment) to the internet, enabling data collection, monitoring, automation, and analysis. IoT applications span industries like healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, and smart cities, enhancing productivity and decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI encompasses various technologies that enable machines to simulate human intelligence, such as natural language processing, computer vision, and decision-making algorithms. ML is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms learning from data to improve performance and make predictions or decisions autonomously.
Big Data Analytics: Involves collecting, processing, and analyzing large volumes of data (structured, semi-structured, unstructured) to uncover insights, patterns, and trends. Big data analytics fuels informed decision-making, personalized experiences, predictive modeling, and business optimization across sectors.
Blockchain Technology: Provides decentralized and secure digital ledgers that record transactions across multiple computers in a tamper-proof manner. Blockchain enables transparency, trust, immutability, and automation for transactions, contracts, supply chains, digital currencies, and identity management.
5G Technology: The fifth-generation wireless technology offers faster speeds, lower latency, and higher bandwidth than previous generations. 5G enables real-time data transmission, supports IoT deployments, enhances mobile connectivity, and fuels innovations like autonomous vehicles, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR).
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Uses software robots or "bots" to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks and workflows within business processes. RPA streamlines operations, reduces human error, increases efficiency, and frees up employees for higher-value tasks.
Cybersecurity Technologies: Include tools, practices, and strategies to protect digital systems, networks, data, and users from cyber threats. With the growing digital footprint, cybersecurity technologies such as encryption, firewalls, threat intelligence, and access controls are crucial for safeguarding assets and privacy.
Edge Computing: Involves processing and analyzing data closer to the source (edge devices) rather than in centralized data centers or the cloud. Edge computing reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth usage, enhances real-time decision-making, and supports IoT applications in remote or bandwidth-constrained environments.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, enhancing real-world experiences (e.g., AR in retail, training). VR creates immersive, artificial environments, often used for simulations, training, gaming, and virtual meetings. Both AR and VR technologies drive engagement, innovation, and new forms of entertainment and communication.
Key business models of the digital economy
ICT has been implemented across all sectors of the economy to improve productivity, expand market reach, and decrease operating expenses. The use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is exemplified by the widespread implementation of broadband connectivity in enterprises, which
Universal coverage for major organizations is prevalent in nearly all nations of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), with rates exceeding 90% even in smaller businesses.
The digital economy has given rise to a variety of new company concepts. Modern ICT has enabled businesses to operate on a larger scale and at longer distances than ever before, but many of these models are similar to traditional ones. This section covers numerous important examples of new business models. Some business models may complement or overlap, such as payment services falling under e-commerce or cloud computing.
The business models presented below are by no means exhaustive. The digital economy's rapid innovation can both create new business models and render existing ones outdated. The digital economy has given rise to several key business models that have reshaped industries and revolutionized how companies operate. Some of the key business models of the digital economy include:
E-commerce: This model involves buying and selling goods or services over the internet. E-commerce platforms like Amazon, Alibaba, and eBay connect buyers and sellers globally, offering a wide range of products and streamlined purchasing experiences.
Fintech: A FinTech business model comprises an intended customer base, operating strategy, and revenue streams. It is a blueprint for a financial technology company. In general, FinTech entities embrace inclusive monetary strategies, thereby facilitating unrestricted consumer access to an extensive array of financial products and services.
Subscription Services: Many digital businesses offer subscription-based services, where customers pay a recurring fee for access to content, software, or other digital products. Examples include Netflix for streaming content and Adobe Creative Cloud for software tools.
Freemium Model: This model offers basic services for free while charging for premium features or content. It attracts a large user base with free offerings and monetizes through upgrades. Examples include Dropbox, Spotify, and many mobile apps.
Sharing Economy: Digital platforms enable peer-to-peer sharing of resources such as accommodations (Airbnb), transportation (Uber, Lyft), and freelance services (Upwork, Fiverr). This model optimizes asset utilization and provides income opportunities for individuals.
Digital Advertising: Online platforms monetize through digital advertising, leveraging user data and targeted ads. Google (via AdWords) and Facebook (via Facebook Ads) are prominent players in this space, offering highly targeted advertising solutions to businesses.
Marketplace Platforms: These platforms facilitate transactions between multiple parties, acting as intermediaries. Examples include Etsy for handmade goods, App Store/Play Store for apps, and stock trading platforms like Robinhood.
Data Monetization: Companies leverage data they collect to derive insights, improve services, and sell data-driven products. Data analytics firms, social media platforms, and IoT companies use this model to create value from data assets.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS): These models offer cloud-based platforms or software accessed over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure. Examples include Salesforce for CRM (SaaS) and AWS/Azure for cloud computing (PaaS).
Introduction to Entrepreneurship and Basics of STEM Entrepreneurship
Understand the types of the entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is a complex and diverse phenomena that takes on several shapes based on the goals, circumstances, and sectors it encompasses. Gaining knowledge about the many forms of entrepreneurship is essential for recognizing the extensive impact of entrepreneurial endeavors on economic growth, societal advancement, and technical breakthroughs. The landscape of entrepreneurship encompasses a wide range of enterprises, from small-scale businesses serving local markets to high-growth startups that are transforming global industries. It also includes socially-driven ventures that tackle urgent environmental or societal issues, as well as entrepreneurial initiatives within established organizations. This diverse landscape offers a wealth of opportunities and complexities. Every form of entrepreneurship possesses distinct attributes, prospects, and difficulties, emphasizing the significance of customized tactics and assistance mechanisms to effectively cultivate entrepreneurial ecosystems. This exploration focuses on the several categories of entrepreneurship, emphasizing their unique characteristics and their role in promoting thriving economies and resilient communities globally.

Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7099/11/1/3
Introduction to STEM fields and their applications in entrepreneurship.
STEM education is an interdisciplinary approach that combines Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics to improve students' STEM literacy, compete in the global economy, and find solutions to everyday problems. It gained prominence in 1957 with the launch of the first artificial satellite, leading to the Sputnik moment and the National Science Foundation's abbreviation of STEM. A recent study identified 10 characteristics of STEM education (Kaya,2023):
- interdisciplinary approach,
- real-life context,
- engineering design process,
- evidence-based decision-making,
- recurrent design,
- step-by-step learning,
- learning from mistakes,
- process-focused learning,
- diverse problem solutions,
- and teamwork support.
The incorporation of STEM fields not only propels advancements in diverse sectors but also has a crucial impact on the formation of entrepreneurial environments globally. STEM education and experience enable individuals to comprehend intricate difficulties, devise inventive solutions, and establish influential enterprises that tackle societal requirements. STEM skills and knowledge are very valuable assets in the field of entrepreneurship. They allow entrepreneurs to utilize advanced technology, perform data-driven analyses, and lead groundbreaking breakthroughs in various areas. The convergence of STEM disciplines and entrepreneurship not only promotes economic expansion but also cultivates a climate of innovation, critical thinking, and ongoing education in the contemporary, ever-changing global economy. This debate delves into the importance of STEM professions and their role in fueling entrepreneurial activities and defining the future of innovation and industry.
Identifying entrepreneurial opportunities within STEM disciplines
Though a STEM degree alone won't guarantee anyone a lucrative career, it is a prerequisite to many STEM job options. The trick is to pay close attention to the cost of that degree and do what you can to make sure anyone gets a quality of education at a price anyone can actually afford, without taking on crushing student debt. (FORBES,2020)
 STEM disciplines offer several entrepreneuria opportunities as a result of their rapid developments and dynamic nature. Here are few crucial domains where entrepreneurial opportunities can be identified within the STEM disciplines:
STEM disciplines offer several entrepreneuria opportunities as a result of their rapid developments and dynamic nature. Here are few crucial domains where entrepreneurial opportunities can be identified within the STEM disciplines:
Source: https://blog.pitsco.com/blog/entrepreneur-stem-skills
Anyone can do entrepreneurial activities in the field of;
- Financial Technology
- Data Science and Analytics
- Technology and Software Development
- Engineering and Manufacturing
- Healthcare and Biotechnology
- Renewable Energy and Sustainability
- STEM Education and Outreach
- Space Exploration and Aerospace
These are only a limited number of fields, and the possibilities in STEM subjects are always changing due to technological progress, societal demands, and global problems. STEM workers that possess a range of abilities, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, cooperation, and adaptability, are in a favorable position to succeed in the dynamic and inventive work settings seen in different industries today.
Examples from STEM-driven big ideas and business.
There are numerous examples of successful STEM entrepreneurship ventures across various industries. Here are a few notable examples:
SpaceX: Founded by Elon Musk, SpaceX is a leading aerospace manufacturer and space transportation company. SpaceX has revolutionized the space industry by developing reusable rocket technology, significantly reducing the cost of space exploration and opening up new opportunities for commercial space missions.
Tesla, Inc.: Another venture led by Elon Musk, Tesla is known for its innovative electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage solutions, and solar products. Tesla has played a key role in popularizing EVs and advancing sustainable energy technologies.
Google (Alphabet Inc.): Google is a prime example of STEM entrepreneurship in the technology sector. Its founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, started Google as a search engine company but expanded it into a global technology conglomerate, offering products and services ranging from search engines and online advertising to cloud computing, autonomous vehicles, and artificial intelligence.
23andMe: Founded by Anne Wojcicki, 23andMe is a biotechnology company that provides direct-to-consumer genetic testing kits. The company leverages advanced genomics and data analytics to offer insights into customers' ancestry, health risks, and genetic traits, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Stripe: Founded by brothers Patrick and John Collison, Stripe is a financial technology (fintech) company that provides online payment processing solutions for businesses. Stripe's user-friendly platform and innovative payment technologies have made it a leader in the digital payments industry, serving millions of businesses worldwide.
Blue Origin: Founded by Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin is a private aerospace manufacturer and spaceflight services company. Blue Origin is focused on developing reusable rocket systems and spacecraft for commercial space tourism, scientific research missions, and satellite launches.
CureVac: A biopharmaceutical company specializing in mRNA-based vaccine technologies, CureVac has gained global recognition for its contributions to the development of mRNA vaccines, including vaccines against COVID-19.
These examples illustrate the wide array of areas and technologies in which STEM entrepreneurship has had substantial effects, including space exploration, electric vehicles, biotechnology, healthcare, finance, and more. STEM entrepreneurs persist in propelling innovation, establishing novel marketplaces, and resolving intricate issues through their business endeavors.
What you need for STEM entrepreneurship:

Source: https://dutchuncles.in/discover/stem-and-entrepreneurship-top-skills-required-for-new-age-entrepreneurs/
Undoubtedly, there is a clear and justified strong demand for STEM. The more we adequately prepare ourselves for professions in this rapidly expanding industry, the more proficiently we will be equipped for the future. In an upcoming era that places greater emphasis on the gig economy, the fields of STEM education and entrepreneurship will be more interconnected than ever before. These proficiencies will extend beyond conventional, secure occupations.
Entrepreneurship skills and STEM education are closely interconnected. The skills necessary to excel in STEM fields, such as creativity, problem-solving, foresight, and adaptability, are equally well-suited for achieving success as an entrepreneur.
Steps to become an STEM based entrepreneur in Digital Economy.
For many individuals, the ultimate aspiration is to become self-employed. Entrepreneurs are often driven by a strong need for creative autonomy, the ability to set their own work schedule, and the flexibility to make independent decisions.
However, there is a significant amount of effort required in the background, and a substantial portion of entrepreneurship revolves around meticulous planning, strategic thinking, and unwavering implementation. If you have harbored a desire to enter the field of entrepreneurship but have not yet made the decision to do so, then here is a comprehensive guide consisting of seven steps that will assist you in becoming an entrepreneur.

Source: https://venturz.co/academy/what-is-the-process-of-entrepreneurship
- Find a profitable business idea
Choose the right product category for your online business to minimize risk and increase success. Use the criteria below to understand pros and cons of the product, ensuring a well-rounded choice for your niche.
What is business idea in reality

Source:Youtube.com, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y_jJ1hsIyd0
- Does your product serve a passion or solve a problem?
Selling products that serve a passion or solve a problem offers advantages such as lower marketing costs, as new customers are actively seeking solutions, reducing the need for heavily marketed products.
- Is this a trend, fad, or growing product category?
Engaging in a passing trend can have risks. A trend can be highly profitable. Secure markets are reliable, whereas expanding markets are optimal. Gaining a clear comprehension of the positioning of your product and niche is crucial in determining your level of success or failure.In order to gain a deeper comprehension of the disparities, let us examine the conceptual development curves and subsequently explore a practical illustration for each category.
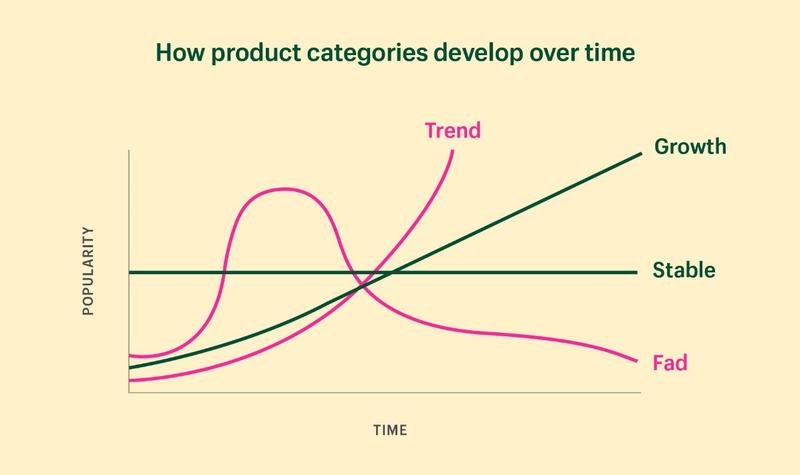
Source: https://www.shopify.com/blog/become-an-entrepreneur
- Get to know your target audience
- Identify and understand the demographics, preferences, behaviors, and needs of your target audience.
- Use market segmentation techniques to divide your audience into distinct groups and tailor your products, services, and marketing efforts accordingly.
- Gather feedback through surveys, interviews, focus groups, or online analytics to gain insights into customer pain points, desires, and expectations.
- Test your idea
- Conduct market research to validate the demand for your product or service.
- Create a prototype or minimum viable product (MVP) to gather feedback from potential customers.
- Test your idea in a controlled environment or through pilot testing to assess feasibility and market acceptance.
- Use a business plan template
- Utilize a business plan template to structure your ideas, goals, strategies, and financial projections.
- Include sections such as executive summary, company description, market analysis, marketing and sales strategies, operations plan, and financial plan in your business plan.
- Develop a product
- Develop your product or service based on customer feedback, market research, and industry best practices.
- Focus on creating value for your target audience and addressing their pain points or needs effectively.
- Validate your product
- Conduct product testing, usability studies, and gather feedback from early adopters or beta testers.
- Evaluate user experience, product performance, and customer satisfaction to make necessary improvements before full-scale launch.
- Write your business plan
- Write a comprehensive business plan detailing your business concept, target market, competitive analysis, marketing and sales strategies, operational processes, and financial projections.
- Ensure that your business plan is well-researched, realistic, and aligns with your long-term goals and objectives.
- Find a secure funding
- Explore different funding options such as bootstrapping, angel investors, venture capital, loans, grants, or crowdfunding depending on your business needs and stage of development.
- Prepare financial documents, pitch decks, and presentations to attract potential investors or lenders.
- Launch your business
- Execute your launch plan including marketing campaigns, sales strategies, distribution channels, and customer acquisition efforts.
- Ensure that your operations, supply chain, and customer support are ready to handle initial demand and deliver a positive customer experience.
- Manage the business
- Implement effective management practices, systems, and processes to streamline operations, monitor performance, and achieve business goals.
- Build and nurture relationships with stakeholders, employees, customers, suppliers, and partners to sustain long-term success.
- Generate value
- Continuously innovate, improve your products or services, and adapt to changing market trends and customer preferences.
- Focus on creating and delivering value to customers, building brand loyalty, and differentiating your business from competitors to generate sustainable growth and profitability.
 Real-World Example for STEM Entrepreneurs:
Real-World Example for STEM Entrepreneurs:
Source: Youtube.com, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GkiK5hBiw6c&list=PPSV
Characteristics of Successful entrepreneurs.
Successful businesspeople can be found in every industry. The importance of paying attention to the entrepreneurial team, rather than focusing on the individual, and the fact that "there's no single personality profile" are both mentioned in Entrepreneurship Essentials. Of course, but there are a few traits and abilities that business owners must possess in order to launch and sustain a successful enterprise.
Listed below are ten traits that prosperous business owners often exhibit.

Source: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/characteristics-of-successful-entrepreneurs
- Curiosity: Entrepreneurs exhibit a distinctive characteristic: curiosity. Their inquisitiveness motivates them to consistently pursue fresh prospects, challenging established norms and investigating alternative paths. Entrepreneurship Essentials defines entrepreneurship as a "process of discovery," emphasizing the significance of curiosity in attaining success.
- Willingness to Experiment: Entrepreneurs need a willingness to experiment and understand structured experimentation, such as design thinking, to determine the worthiness of new opportunities. Conducting thorough market research and conducting meaningful tests is crucial for validating and determining the potential of an idea.
- Adaptability: Entrepreneurship is an iterative process, requiring adaptability and flexibility for successful business leaders to navigate new challenges and opportunities.
- Decisiveness: Entrepreneurs must make difficult decisions and lead their business, guiding funding, strategy, and resource allocation. Confidence is crucial for making these decisions, even if the outcome isn't favorable, and corrective action is necessary.
- Self-Awareness: Great entrepreneurs recognize their strengths and weaknesses, building well-rounded teams to complement their abilities. Surrounding yourself with teammates with complementary talents drives business venture success.
- Risk Tolerance: Entrepreneurship involves risk, but it's essential to minimize it. Successful entrepreneurs manage the relationship between risk and reward, positioning their companies to benefit from the upside. Their risk tolerance is closely linked to their efforts to mitigate it.
- Comfort with Failure: Entrepreneurship necessitates risk-management and decision-making, as 70% of startups survive at least two years, half last five, and a quarter last 15 years. Failures can arise from various factors, including business scalability and low product-market fit. Entrepreneurs must prepare for and be comfortable with failure, maintaining a positive attitude for success.
- Persistence: Successful entrepreneurs view failure as an opportunity for growth and learning, despite the possibility of failure. They persist, ask questions, and learn from mistakes to achieve their goals.
- İnnovative Thinking: Innovation is a strategic mindset that can be cultivated by entrepreneurs, as it involves novel and useful ideas, not necessarily new products or services. Successful startups often improve existing products to meet market needs.
- Long-Term Focus: Entrepreneurship is not just about starting a business; it involves a long-term journey, from securing funding to identifying and leveraging opportunities. It's not just about starting a business; it's about growing it sustainably.
Real-World Examples for Characteristics of Successful Entrepreneurs:

Source: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/characteristics-of-successful-entrepreneurs
Conclusion
STEM-based entrepreneurship is crucial in driving innovation, creating value, and defining the future of industries worldwide in the fast changing digital economy. The integration of STEM subjects with entrepreneurial pursuits has resulted in revolutionary advancements, disruptive innovations, and transforming business models. When considering the influence of STEM-based entrepreneurship in the digital era, we may identify three important observations.
First and foremost, knowledge in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) provides the fundamental basis for digital innovation and entrepreneurship. Proficiencies in coding, data analytics, artificial intelligence, robotics, and cybersecurity are not only highly sought after but also crucial for the advancement of state-of-the-art products, services, and solutions. Entrepreneurs that have a solid foundation in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) has the expertise and skills needed to tackle intricate problems and take advantage of new possibilities in the digital economy.
Furthermore, STEM-based entrepreneurship promotes collaboration across different disciplines and partnerships between other sectors. Integrating STEM with sectors including healthcare, banking, education, agriculture, and renewable energy results in diverse solutions that enhance efficiency, sustainability, and societal impact. Collaborative ecosystems, which consist of startups, research institutions, businesses, governments, and investors, play a crucial role in driving innovation and providing support for enterprises that can grow rapidly.
In addition, STEM entrepreneurship flourishes in digital ecosystems that are defined by digital platforms, cloud computing, big data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and automation technologies. These digital tools give entrepreneurs unparalleled access to international marketplaces, valuable customer information, flexible development resources, and expandable infrastructure, creating a fairer environment for new businesses and promoting entrepreneurial innovation.
In addition, STEM-based entrepreneurship in the digital economy encompasses not only technological expertise but also a focus on customer needs, user satisfaction, and ethical concerns. Thriving enterprises place a high value on comprehending customer requirements, safeguarding data privacy, ensuring cybersecurity, and responsibly implementing AI technology. By doing so, they cultivate trust and loyalty in a world that is becoming more interconnected and reliant on data.
In the coming years, STEM-based entrepreneurship will persist in propelling digital transformation, economic expansion, and sustainable development. By providing education, mentorship, funding opportunities, and supportive legislation, we can empower the upcoming generation of STEM entrepreneurs. This will stimulate innovation ecosystems and help tackle global concerns such as climate change, healthcare, and inclusive economic prosperity.STEM-based entrepreneurship serves as both an economic driver and a catalyst for positive change, empowerment, and human growth in the digital era.
Quizzes
External resources
- Deloitte. "Digital Transformation: Rewriting the rules of business." Deloitte Insights, 2021.
- IDC. "IDC FutureScape: Worldwide Digital Transformation 2022 Predictions." IDC, 2022.
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/impact-digitization-shantanu-garg
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/digital-economy
- https://www2.deloitte.com/mt/en/pages/technology/articles/mt-what-is-digital-economy.html
- https://www.ir.com/guides/the-importance-of-the-digital-economy
- https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/9789264218789-7-en.pdf?expires=1710930428&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=F5AE5C75FF90B0577DAD5DEFE5A64C00
- https://www.wix.com/blog/types-of-entrepreneurship
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2020/08/25/entrepreneurship-key-to-future-success-in-stem/?sh=dbe7bf25b27c
- Kaya, S.(2023). The New Trends in Entrepreneurship and STEM Education Studies: A
- Bibliometric Study. Inonu University, Faculty of Education. Vol:24, No:2. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/3233155
- https://www.wegate.eu/female-entrepreneurs-in-stem/
- https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/characteristics-of-successful-entrepreneurs
- https://www.shopify.com/blog/become-an-entrepreneur
- https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7099/11/1/3
- Lee, S.C. and Nicholas, S. (2022). Business Model Innovation in the Digital Economy.